ISO/TR 24971:2020
(Main)Medical devices — Guidance on the application of ISO 14971
Medical devices — Guidance on the application of ISO 14971
This document provides guidance on the development, implementation and maintenance of a risk management system for medical devices according to ISO 14971:2019. The risk management process can be part of a quality management system, for example one that is based on ISO 13485:2016[24], but this is not required by ISO 14971:2019. Some requirements in ISO 13485:2016 (Clause 7 on product realization and 8.2.1 on feedback during monitoring and measurement) are related to risk management and can be fulfilled by applying ISO 14971:2019. See also the ISO Handbook: ISO 13485:2016 — Medical devices — A practical guide[25].
Dispositifs médicaux — Recommandations relatives à l'application de l'ISO 14971
Le présent document fournit des recommandations relatives au développement, à la mise en œuvre et à la tenue à jour d'un système de gestion des risques pour les dispositifs médicaux conformément à l'ISO 14971:2019. Le processus de gestion des risques peut faire partie d'un système de management de la qualité qui s'appuie, par exemple, sur l'ISO 13485:2016[24], mais cela n'est pas requis par l'ISO 14971:2019. Certaines exigences de l'ISO 13485:2016 (Article 7 relatif à la réalisation du produit et 8.2.1[eXtyles1] relatives aux retours d'information au cours de la surveillance et du mesurage) portent sur la gestion des risques et peuvent être satisfaites en appliquant l'ISO 14971:2019. Voir également le manuel ISO: ISO 13485:2016 — Medical devices — A practical guide[25]. [eXtyles1]No section matches the in-text citation "8.2.1". Please supply the missing section or delete the citation.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
TECHNICAL ISO/TR
REPORT 24971
Second edition
2020-05
Medical devices — Guidance on the
application of ISO 14971
Dispositifs médicaux — Directives relatives à l'ISO 14971
PROOF/ÉPREUVE
Reference number
©
ISO 2020
© ISO 2020
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, or required in the context of its implementation, no part of this publication may
be reproduced or utilized otherwise in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, or posting
on the internet or an intranet, without prior written permission. Permission can be requested from either ISO at the address
below or ISO’s member body in the country of the requester.
ISO copyright office
CP 401 • Ch. de Blandonnet 8
CH-1214 Vernier, Geneva
Phone: +41 22 749 01 11
Fax: +41 22 749 09 47
Email: copyright@iso.org
Website: www.iso.org
Published in Switzerland
ii PROOF/ÉPREUVE © ISO 2020 – All rights reserved
Contents Page
Foreword .v
Introduction .vi
1 Scope . 1
2 Normative references . 1
3 Terms and definitions . 1
4 General requirements for risk management system . 1
4.1 Risk management process . 1
4.2 Management responsibilities . 1
4.2.1 Top management commitment . 1
4.2.2 Policy for establishing criteria for risk acceptability . 2
4.2.3 Suitability of the risk management process . 2
4.3 Competence of personnel . 2
4.4 Risk management plan . 3
4.4.1 General. 3
4.4.2 Scope of the risk management plan . 4
4.4.3 Assignment of responsibilities and authorities . 4
4.4.4 Requirements for review of risk management activities . 4
4.4.5 Criteria for risk acceptability . 4
4.4.6 Method to evaluate overall residual risk and criteria for acceptability . 4
4.4.7 Verification activities . 5
4.4.8 Activities related to collection and review of production and post-
production information . 5
4.5 Risk management file . 5
5 Risk analysis . 6
5.1 Risk analysis process . 6
5.2 Intended use and reasonably foreseeable misuse . 6
5.3 Identification of characteristics related to safety . 7
5.4 Identification of hazards and hazardous situations . 7
5.4.1 Hazards . 7
5.4.2 Hazardous situations in general . 7
5.4.3 Hazardous situations resulting from faults . 8
5.4.4 Hazardous situations resulting from random faults . 8
5.4.5 Hazardous situations resulting from systematic faults . 8
5.4.6 Hazardous situations arising from security vulnerabilities . 9
5.4.7 Sequences or combinations of events . 9
5.5 Risk estimation .11
5.5.1 General.11
5.5.2 Probability .12
5.5.3 Risks for which probability cannot be estimated .12
5.5.4 Severity .13
5.5.5 Examples .13
6 Risk evaluation .15
7 Risk control .15
7.1 Risk control option analysis .15
7.1.1 Risk control for medical device design .15
7.1.2 Risk control for manufacturing processes .17
7.1.3 Standards and risk control .18
7.2 Implementation of risk control measures .18
7.3 Residual risk evaluation .18
7.4 Benefit-risk analysis .18
7.4.1 General.18
7.4.2 Benefit estimation .19
7.4.3 Criteria for benefit-risk analysis .20
7.4.4 Benefit-risk comparison.20
7.4.5 Examples of benefit-risk analyses .20
7.5 Risks arising from risk control measures .21
7.6 Completeness of risk control .21
8 Evaluation of overall residual risk .21
8.1 General considerations .21
8.2 Inputs and other considerations .22
8.3 Possible approaches .23
9 Risk management review .24
10 Production and post-production activities.24
10.1 General .24
10.2 Information collection .24
10.3 Information review .26
10.4 Actions .27
Annex A (informative) Identification of hazards and characteristics related to safety .29
Annex B (informative) Techniques that support risk analysis .37
Annex C (informative) Relation between the policy, criteria for risk acceptability,risk
control and risk evaluation .42
Annex D (informative) Information for safety and information on residual risk .47
Annex E (informative) Role of international standards in risk management .50
Annex F (informative) Guidance on risks related to security .55
Annex G (informative) Components and devices designed without using ISO 14971 .60
Annex H (informative) Guidance for in vitro diagnostic medical devices .62
Bibliography .85
iv PROOF/ÉPREUVE © ISO 2020 – All rights reserved
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards
bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out
through ISO technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical
committee has been established has the right
...
TECHNICAL ISO/TR
REPORT 24971
Second edition
2020-06
Medical devices — Guidance on the
application of ISO 14971
Dispositifs médicaux — Recommandations relatives à l'application de
l'ISO 14971
Reference number
©
ISO 2020
© ISO 2020
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, or required in the context of its implementation, no part of this publication may
be reproduced or utilized otherwise in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, or posting
on the internet or an intranet, without prior written permission. Permission can be requested from either ISO at the address
below or ISO’s member body in the country of the requester.
ISO copyright office
CP 401 • Ch. de Blandonnet 8
CH-1214 Vernier, Geneva
Phone: +41 22 749 01 11
Email: copyright@iso.org
Website: www.iso.org
Published in Switzerland
ii © ISO 2020 – All rights reserved
Contents Page
Foreword .v
Introduction .vi
1 Scope . 1
2 Normative references . 1
3 Terms and definitions . 1
4 General requirements for risk management system . 1
4.1 Risk management process . 1
4.2 Management responsibilities . 1
4.2.1 Top management commitment . 1
4.2.2 Policy for establishing criteria for risk acceptability . 2
4.2.3 Suitability of the risk management process . 2
4.3 Competence of personnel . 2
4.4 Risk management plan . 3
4.4.1 General. 3
4.4.2 Scope of the risk management plan . 4
4.4.3 Assignment of responsibilities and authorities . 4
4.4.4 Requirements for review of risk management activities . 4
4.4.5 Criteria for risk acceptability . 4
4.4.6 Method to evaluate overall residual risk and criteria for acceptability . 5
4.4.7 Verification activities . 5
4.4.8 Activities related to collection and review of production and post-
production information . 5
4.5 Risk management file . 5
5 Risk analysis . 6
5.1 Risk analysis process . 6
5.2 Intended use and reasonably foreseeable misuse . 6
5.3 Identification of characteristics related to safety . 7
5.4 Identification of hazards and hazardous situations . 7
5.4.1 Hazards . 7
5.4.2 Hazardous situations in general . 8
5.4.3 Hazardous situations resulting from faults . 8
5.4.4 Hazardous situations resulting from random faults . 8
5.4.5 Hazardous situations resulting from systematic faults . 8
5.4.6 Hazardous situations arising from security vulnerabilities . 9
5.4.7 Sequences or combinations of events . 9
5.5 Risk estimation .11
5.5.1 General.11
5.5.2 Probability .12
5.5.3 Risks for which probability cannot be estimated .13
5.5.4 Severity .13
5.5.5 Examples .13
6 Risk evaluation .16
7 Risk control .16
7.1 Risk control option analysis .16
7.1.1 Risk control for medical device design .16
7.1.2 Risk control for manufacturing processes .18
7.1.3 Standards and risk control .19
7.2 Implementation of risk control measures .19
7.3 Residual risk evaluation .19
7.4 Benefit-risk analysis .19
7.4.1 General.19
7.4.2 Benefit estimation .20
7.4.3 Criteria for benefit-risk analysis .21
7.4.4 Benefit-risk comparison.21
7.4.5 Examples of benefit-risk analyses .21
7.5 Risks arising from risk control measures .22
7.6 Completeness of risk control .22
8 Evaluation of overall residual risk .22
8.1 General considerations .22
8.2 Inputs and other considerations .23
8.3 Possible approaches .24
9 Risk management review .25
10 Production and post-production activities.25
10.1 General .25
10.2 Information collection .25
10.3 Information review .27
10.4 Actions .28
Annex A (informative) Identification of hazards and characteristics related to safety .30
Annex B (informative) Techniques that support risk analysis .38
Annex C (informative) Relation between the policy, criteria for risk acceptability, risk
control and risk evaluation .43
Annex D (informative) Information for safety and information on residual risk .48
Annex E (informative) Role of international standards in risk management .51
Annex F (informative) Guidance on risks related to security .56
Annex G (informative) Components and devices designed without using ISO 14971 .61
Annex H (informative) Guidance for in vitro diagnostic medical devices .63
Bibliography .86
iv © ISO 2020 – All rights reserved
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards
bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out
through ISO technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical
committee has been established has the right to be represented on that committee. International
organiza
...
TECHNICAL ISO/TR
REPORT 24971
Redline version
compares Second edition to
First edition
Medical devices — Guidance on the
application of ISO 14971
Dispositifs médicaux — Recommandations relatives à l'application
de l'ISO 14971
Reference number
ISO/TR 24971:redline:2020(E)
©
ISO 2020
ISO/TR 24971:redline:2020(E)
IMPORTANT
This marked-up version uses the following colour-coding in the marked-up text:
Text example 1 — Text has been added (in green)
— Text has been deleted (in red)
Text example 2
— Graphic figure has been added
— Graphic figure has been deleted
1.x . — If there are changes in a clause/subclause, the corresponding clause/
subclause number is highlighted in yellow in the Table of contents
DISCLAIMER
This marked-up version highlights the main changes in this edition of the document
compared with the previous edition. It does not focus on details (e.g. changes in
punctuation).
This marked-up version does not constitute the official ISO document and is not intended to
be used for implementation purposes.
© ISO 2020
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, or required in the context of its implementation, no part of this publication may
be reproduced or utilized otherwise in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, or posting
on the internet or an intranet, without prior written permission. Permission can be requested from either ISO at the address
below or ISO’s member body in the country of the requester.
ISO copyright office
CP 401 • Ch. de Blandonnet 8
CH-1214 Vernier, Geneva
Phone: +41 22 749 01 11
Fax: +41 22 749 09 47
Email: copyright@iso.org
Website: www.iso.org
Published in Switzerland
ii © ISO 2020 – All rights reserved
ISO/TR 24971:redline:2020(E)
Contents Page
Foreword .v
Introduction .vi
1 Scope . 1
2 Normative references . 1
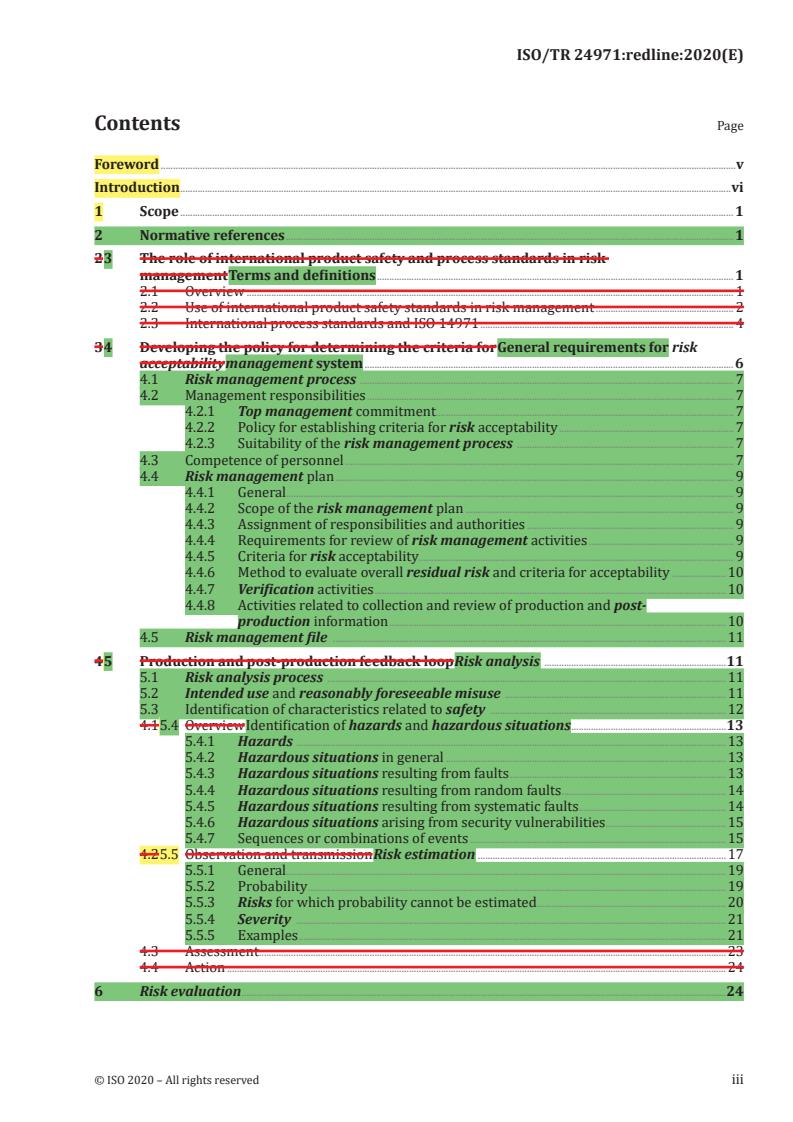
2 3 The role of international product safety and process standards in risk
management Terms and definitions . 1
2.1 Overview . 1
2.2 Use of international product safety standards in risk management . 2
2.3 International process standards and ISO 14971 . 4
3 4 Developing the policy for determining the criteria for General requirements for risk
acceptability management system . 6
4.1 Risk management process . 7
4.2 Management responsibilities . 7
4.2.1 Top management commitment . 7
4.2.2 Policy for establishing criteria for risk acceptability . 7
4.2.3 Suitability of the risk management process . 7
4.3 Competence of personnel . 7
4.4 Risk management plan . 9
4.4.1 General. 9
4.4.2 Scope of the risk management plan . 9
4.4.3 Assignment of responsibilities and authorities . 9
4.4.4 Requirements for review of risk management activities . 9
4.4.5 Criteria for risk acceptability . 9
4.4.6 Method to evaluate overall residual risk and criteria for acceptability .10
4.4.7 Verification activities .10
4.4.8 Activities related to collection and review of production and post-
production information .10
4.5 Risk management file .11
4 5 Production and post-production feedback loop Risk analysis .11
5.1 Risk analysis process .11
5.2 Intended use and reasonably foreseeable misuse .11
5.3 Identification of characteristics related to safety .12
4.1 5.4 Overview Identification of hazards and hazardous situations .13
5.4.1 Hazards .13
5.4.2 Hazardous situations in general .13
5.4.3 Hazardous situations resulting from faults .13
5.4.4 Hazardous situations resulting from random faults .14
5.4.5 Hazardous situations resulting from systematic faults .14
5.4.6 Hazardous situations arising from security vulnerabilities .15
5.4.7 Sequences or combinations of events .15
4.2 5.5 Observation and transmission Risk estimation .17
5.5.1 General.19
5.5.2 Probability .19
5.5.3 Risks for which probability cannot be estimated .20
5.5.4 Severity .21
5.5.5 Examples .21
4.3 Assessment .23
4.4 Action .24
6 Risk evaluation .24
ISO/TR 24971:redline:2020(E)
5 7 Differentiation of information for safety and disclosure of residual risk Risk control .24
7.1 Risk control option analysis .24
7.1.1 Risk control for medical device design .24
7.1.2 Risk control for manufacturing processes .26
7.1.3 Standards and risk control .27
7.2 Implementation of risk control measures .27
7.3 Residual risk evaluation .27
5.1 7.4 Difference between “information for safety” and “disclosure of residual risk”
Benefit-risk analysis .27
7.4.1 General.28
7.4.2 Benefit estimation .28
7.4.3 Criteria for benefit-risk analysis .29
7.4.4 Benefit-risk comparison.29
7.4.5 Examples of benefit-risk analyses .30
5.2 Information for safety .30
5.3 7.5 Disclosure of residual risk Risks arising from risk control measures .30
7.6 Completeness of risk control .31
6 8 Evaluation of overall residual risk .31
6.1 8.1 Overview General considerations.31
8.2 Inputs and other considerations .32
6.2 8.3 Inputs and other considerations for overall residual risk evaluation Possible
approaches .33
9 Risk management review .35
10 Production and post-production activities.35
10.1 General .35
10.2 Information collection .35
10.3 Information review .37
10.4 Actions .38
Annex A (informative) Identification of hazards and characteristics related to s
...
RAPPORT ISO/TR
TECHNIQUE 24971
Deuxième édition
2020-06
Dispositifs médicaux —
Recommandations relatives à
l'application de l'ISO 14971
Medical devices — Guidance on the application of ISO 14971
Numéro de référence
©
ISO 2020
DOCUMENT PROTÉGÉ PAR COPYRIGHT
© ISO 2020
Tous droits réservés. Sauf prescription différente ou nécessité dans le contexte de sa mise en œuvre, aucune partie de cette
publication ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mécanique,
y compris la photocopie, ou la diffusion sur l’internet ou sur un intranet, sans autorisation écrite préalable. Une autorisation peut
être demandée à l’ISO à l’adresse ci-après ou au comité membre de l’ISO dans le pays du demandeur.
ISO copyright office
Case postale 401 • Ch. de Blandonnet 8
CH-1214 Vernier, Genève
Tél.: +41 22 749 01 11
E-mail: copyright@iso.org
Web: www.iso.org
Publié en Suisse
ii © ISO 2020 – Tous droits réservés
Sommaire Page
Avant-propos .v
Introduction .vi
1 Domaine d’application . 1
2 Références normatives . 1
3 Termes et définitions . 1
4 Exigences générales relatives au système de gestion des risques . 1
4.1 Processus de gestion des risques. 1
4.2 Responsabilités de la direction . 2
4.2.1 Implication de la direction . 2
4.2.2 Politique d’établissement des critères d’acceptabilité du risque . 2
4.2.3 Adéquation du processus de gestion des risques . 2
4.3 Compétence du personnel . 2
4.4 Plan de gestion des risques . 4
4.4.1 Généralités . 4
4.4.2 Champ d’application du plan de gestion des risques . 4
4.4.3 Attribution des responsabilités et des autorités . 5
4.4.4 Exigences relatives à l’examen des activités de gestion des risques. 5
4.4.5 Critères d’acceptabilité du risque . 5
4.4.6 Méthode d’évaluation du risque résiduel global et critères d’acceptabilité . 5
4.4.7 Activités de vérification. 5
4.4.8 Activités associées à la collecte et à l’examen des informations de
production et de postproduction . 6
4.5 Dossier de gestion des risques . 6
5 Analyse des risques . 7
5.1 Processus d’analyse des risques . 7
5.2 Utilisation prévue et mauvaise utilisation raisonnablement prévisible . 7
5.3 Identification des caractéristiques relatives à la sécurité . 8
5.4 Identification des dangers et des situations dangereuses . 9
5.4.1 Dangers . 9
5.4.2 Situations dangereuses en général . 9
5.4.3 Situations dangereuses résultant de défaillances . 9
5.4.4 Situations dangereuses résultant de défaillances aléatoires . 9
5.4.5 Situations dangereuses résultant de défaillances systématiques .10
5.4.6 Situations dangereuses découlant de vulnérabilités de sûreté .10
5.4.7 Séquences ou combinaisons d’événements .11
5.5 Estimation des risques .13
5.5.1 Généralités .13
5.5.2 Probabilité .14
5.5.3 Risques pour lesquels la probabilité ne peut pas être estimée .15
5.5.4 Gravité .16
5.5.5 Exemples .16
6 Évaluation des risques .19
7 Maîtrise des risques .19
7.1 Analyse des options de maîtrise des risques .19
7.1.1 Maîtrise des risques lors de la conception de dispositifs médicaux .19
7.1.2 Maîtrise des risques lors des processus de fabrication .21
7.1.3 Normes et maîtrise des risques .22
7.2 Mise en œuvre des mesures de maîtrise des risques .22
7.3 Évaluation des risques résiduels .22
7.4 Analyse du bénéfice/risque .23
7.4.1 Généralités .23
7.4.2 Estimation des bénéfices .23
7.4.3 Critères pour l’analyse du bénéfice/risque .24
7.4.4 Comparaison du bénéfice/risque .24
7.4.5 Exemples d’analyses du bénéfice/risque .25
7.5 Risques découlant des mesures de maîtrise des risques .26
7.6 Maîtrise complète des risques .26
8 Évaluation du risque résiduel global .26
8.1 Considérations générales .26
8.2 Éléments d’entrée et autres considérations .27
8.3 Approches possibles.28
9 Revue de la gestion des risques .29
10 Activités de production et de postproduction .30
10.1 Généralités .30
10.2 Collecte des informations .30
10.3 Examen des informations .32
10.4 Actions .33
Annexe A (informative) Identification des dangers et des caractéristiques relatives à la sécurité.35
Annexe B (informative) Techniques visant à étayer une analyse des risques .44
Annexe C (informative) Relation entre la politique, les critères d’acceptabilité du risque, la
maîtrise des risques et l’évaluation des risques .50
Annexe D (informative) Informations relatives à la sécurité et au risque résiduel .56
Annexe E (informative) Rôle des normes internationales dans la gestion des risques .59
Annexe F (informative) Recommandations concernant les risques relatifs à la sûreté .65
Annexe G (informative) Composants et dispositifs conçus sans recourir à l’ISO 14971 .70
Annexe H (informative) Recommandations pour les dispositifs médicaux de diagnostic in vitro .73
Bibliographie .103
iv © ISO 2020 – Tous droits réservés
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale d’organismes
nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de l’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est
en général confiée aux comités techniques de l’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude
a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales,
gouvernementales et non gouvernementales, en liaison avec l’ISO participent également aux travaux.
L’ISO collabore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (IEC) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les procédures utilisées pour élaborer le présent document et celles destinées à sa mise à jour sont
décrites dans les Directives ISO/IEC, Partie 1. Il convient, en particulier de prendre note des différents
critères d’approbation requis pour les différents types de documents ISO. Le présent document a été
rédigé conformément aux règles de rédaction données dans les Directives ISO/IEC, Partie 2 (voir www
.iso .org/ directives).
L’attention est attirée sur le fait que certains des éléments du présent document peuvent faire l’objet de
d
...













Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.